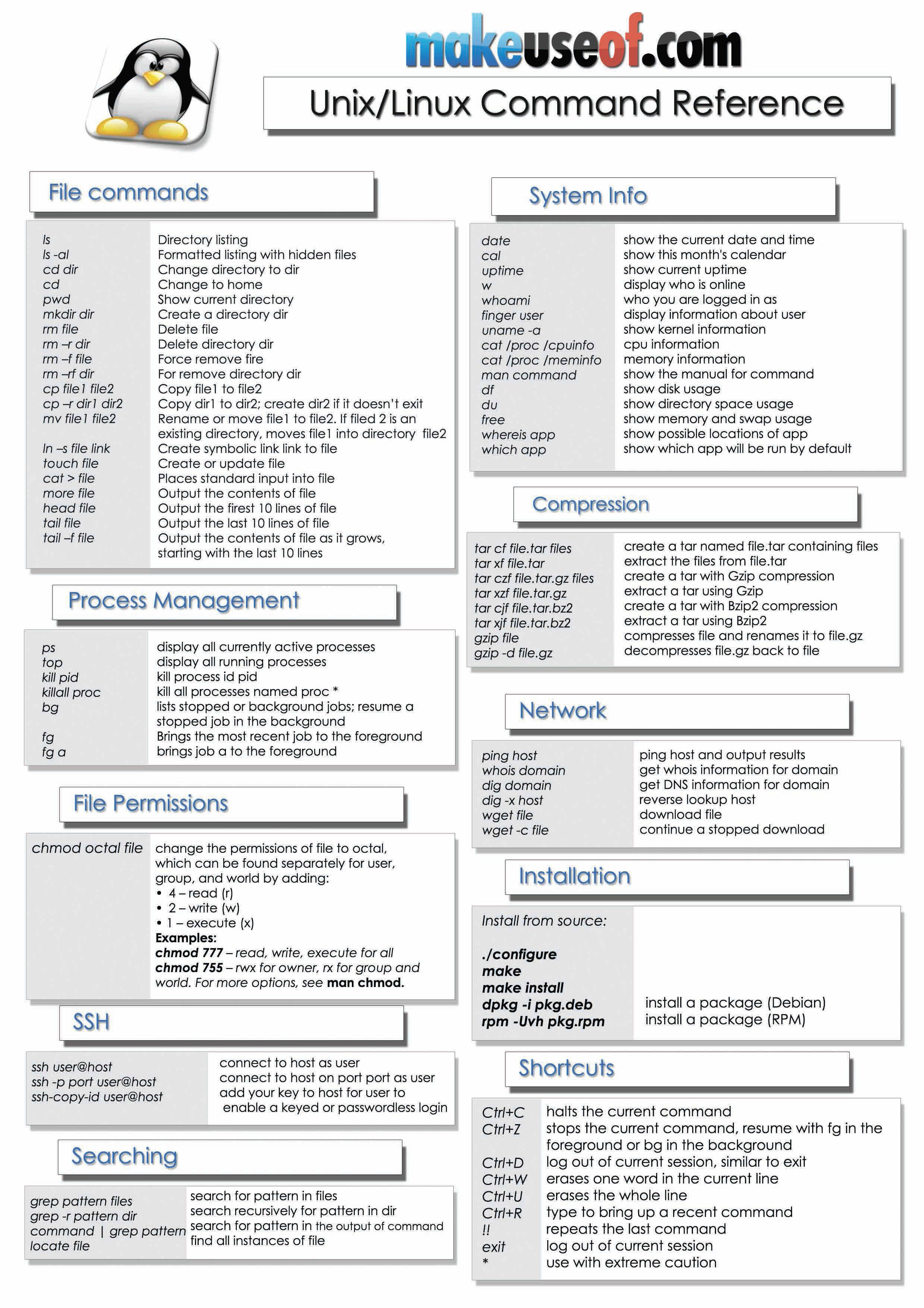
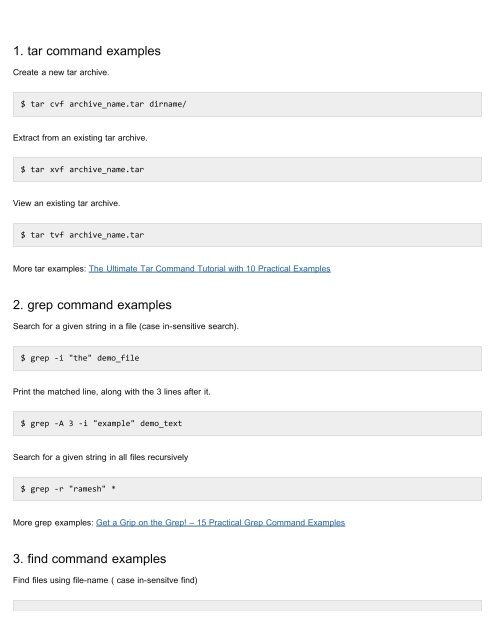
UNIX commands, however, are stand-alone programs; they may incorporate both system calls and library functions in their programming. 21) What is Bash Shell? It is a free shell designed to work on the UNIX system. Being the default shell for most UNIX-based systems, it combines features that are available both in the C and Korn Shell. In Unix/Linux, software is installed in the form of packages. A package contains the program itself. Any dependent component needs to be downloaded separately. You can also send e-mails from terminal using the 'mail' command; Cheat Sheet. Below is a Cheat Sheet of Linux commands we have learned in this tutorial.
- Basic Unix Commands Cheat Sheet.pdf
- Unix Basics Commands Pdf With Example
- Basic Unix Linux Commands Pdf
- Basic Unix Commands For Beginners Pdf
- Basic Unix Administration Commands Pdf
The first character, the type field, indicates the file type. In the example above the file type is “-”, which indicates a regular file. Other file types include: d for directory, l (lower case ell) for symbolic link, s for Unix domain socket, p for named pipe, c for character device file and b for block device file. This tutorial is written to help people understand some of the basics of shell script programming (aka shell scripting), and hopefully to introduce some of the possibilities of simple but powerful programming available under the Bourne shell. As such, it has been written as a basis for one-on-one or group tutorials and exercises, and as a reference for subsequent use. Compiled by Aluizio using the book UNIX IN A NUTSHELL, Arnold Robbins, O'Reilly Ed., 4th edition, 2005, ISBN 0596100299. USEFUL UNIX COMMANDS cancel cancel print requested with lp cat file Display the file cat file1 file2 files Combine file1 and file2 into files. Some Basic UNIX Commands by Donald Hyatt The UNIX operating system has for many years formed the backbone of the Internet, especially for large servers and most major university campuses. File Access Modes The permissions of a file are the first line of defense in the security of a Unix system. The basic building blocks of Unix permissions are the read, write, and execute permissions, which have been described below − Read. Grants the capability to read, i.e., view the contents of the file.
This is a list of Unix commands as specified by IEEE Std 1003.1-2008, which is part of the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). These commands can be found on Unix operating systems and most Unix-like operating systems.
List[edit]
| Name | Category | Status (Option code) | Description | First appeared |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| admin | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Create and administer SCCS files | PWB UNIX |
| alias | Misc | Mandatory | Define or display aliases | |
| ar | Misc | Mandatory | Create and maintain library archives | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| asa | Text processing | Optional (FR) | Interpret carriage-control characters | System V |
| at | Process management | Mandatory | Execute commands at a later time | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| awk | Text processing | Mandatory | Pattern scanning and processing language | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| basename | Filesystem | Mandatory | Return non-directory portion of a pathname; see also dirname | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| batch | Process management | Mandatory | Schedule commands to be executed in a batch queue | |
| bc | Misc | Mandatory | Arbitrary-precision arithmetic language | Version 6 AT&T UNIX |
| bg | Process management | Optional (UP) | Run jobs in the background | |
| cc/c99 | C programming | Optional (CD) | Compile standard C programs | IEEE Std 1003.1-2001 |
| cal | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Print a calendar | Version 5 AT&T UNIX |
| cat | Filesystem | Mandatory | Concatenate and print files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| cd | Filesystem | Mandatory | Change the working directory | Version 6 AT&T UNIX |
| cflow | C programming | Optional (XSI) | Generate a C-language call graph | System V |
| chgrp | Filesystem | Mandatory | Change the file group ownership | PWB UNIX |
| chmod | Filesystem | Mandatory | Change the file modes/attributes/permissions | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| chown | Filesystem | Mandatory | Change the file ownership | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| cksum | Filesystem | Mandatory | Write file checksums and sizes | 4.4BSD |
| cmp | Filesystem | Mandatory | Compare two files; see also diff | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| comm | Text processing | Mandatory | Select or reject lines common to two files | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| command | Shell programming | Mandatory | Execute a simple command | |
| compress | Filesystem | Optional (XSI) | Compress data | 4.3BSD |
| cp | Filesystem | Mandatory | Copy files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| crontab | Misc | Mandatory | Schedule periodic background work | System V |
| csplit | Text processing | Mandatory | Split files based on context | PWB UNIX |
| ctags | C programming | Optional (SD) | Create a tags file | 3BSD |
| cut | Text processing | Mandatory | Cut out selected fields of each line of a file | System III |
| cxref | C programming | Optional (XSI) | Generate a C-language program cross-reference table | System V |
| date | Misc | Mandatory | Display the date and time | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| dd | Filesystem | Mandatory | Convert and copy a file | Version 5 AT&T UNIX |
| delta | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Make a delta (change) to an SCCS file | PWB UNIX |
| df | Filesystem | Mandatory | Report free disk space | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| diff | Text processing | Mandatory | Compare two files; see also cmp | Version 5 AT&T UNIX |
| dirname | Filesystem | Mandatory | Return the directory portion of a pathname; see also basename | System III |
| du | Filesystem | Mandatory | Estimate file space usage | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| echo | Shell programming | Mandatory | Write arguments to standard output | Version 2 AT&T UNIX |
| ed | Text processing | Mandatory | The standard text editor | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| env | Misc | Mandatory | Set the environment for command invocation | System III |
| ex | Text processing | Optional (XSI) | Text editor | 1BSD |
| expand | Text processing | Mandatory | Convert tabs to spaces | 3BSD |
| expr | Shell programming | Mandatory | Evaluate arguments as an expression | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| false | Shell programming | Mandatory | Return false value | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| fc | Misc | Optional (UP) | Process the command history list | |
| fg | Process management | Optional (UP) | Run jobs in the foreground | |
| file | Filesystem | Mandatory | Determine file type | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| find | Filesystem | Mandatory | Find files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| fold | Text processing | Mandatory | Filter for folding lines | 1BSD |
| fort77 | FORTRAN77 programming | Obsolescent (FD) | FORTRAN compiler | XPG4 |
| fuser | Process management | Optional (XSI) | List process IDs of all processes that have one or more files open | System V |
| gencat | Misc | Mandatory | Generate a formatted message catalog | |
| get | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Get a version of an SCCS file | PWB UNIX |
| getconf | Misc | Mandatory | Get configuration values | |
| getopts | Shell programming | Mandatory | Parse utility options | |
| grep | Misc | Mandatory | Search text for a pattern | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| hash | Misc | Mandatory | hash database access method | |
| head | Text processing | Mandatory | Copy the first part of files | PWB UNIX[citation needed] |
| iconv | Text processing | Mandatory | Codeset conversion | HP-UX |
| id | Misc | Mandatory | Return user identity | System V |
| ipcrm | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Remove a message queue, semaphore set, or shared memory segment identifier | System V |
| ipcs | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Report interprocess communication facilities status | System V |
| jobs | Process management | Optional (UP) | Display status of jobs in the current session | |
| join | Text processing | Mandatory | Merges two sorted text files based on the presence of a common field | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| kill | Process management | Mandatory | Terminate or signal processes | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| lex | C programming | Optional (CD) | Generate programs for lexical tasks | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| link | Filesystem | Optional (XSI) | Create a hard link to a file | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| ln | Filesystem | Mandatory | Link files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| locale | Misc | Mandatory | Get locale-specific information | |
| localedef | Misc | Mandatory | Define locale environment | |
| logger | Shell programming | Mandatory | Log messages | 4.3BSD |
| logname | Misc | Mandatory | Return the user's login name | 4.4BSD |
| lp | Text processing | Mandatory | Send files to a printer | System V |
| ls | Filesystem | Mandatory | List directory contents | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| m4 | Misc | Mandatory | Macro processor | PWB UNIX |
| mailx | Misc | Mandatory | Process messages | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| make | Programming | Optional (SD) | Maintain, update, and regenerate groups of programs | PWB UNIX |
| man | Misc | Mandatory | Display system documentation | Version 2 AT&T UNIX |
| mesg | Misc | Mandatory | Permit or deny messages | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| mkdir | Filesystem | Mandatory | Make directories | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| mkfifo | Filesystem | Mandatory | Make FIFO special files | 4.4BSD[dubious] |
| more | Text processing | Optional (UP) | Display files on a page-by-page basis | 3BSD |
| mv | Filesystem | Mandatory | Move or rename files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| newgrp | Misc | Mandatory | Change to a new group (functionality similar to sg[1]) | Version 6 AT&T UNIX |
| nice | Process management | Mandatory | Invoke a utility with an altered nice value | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| nl | Text processing | Optional (XSI) | Line numbering filter | System III |
| nm | C programming | Optional (SD, XSI) | Write the name list of an object file | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| nohup | Process management | Mandatory | Invoke a utility immune to hangups | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| od | Misc | Mandatory | Dump files in various formats | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| paste | Text processing | Mandatory | Merge corresponding or subsequent lines of files | Version 32V AT&T UNIX |
| patch | Text processing | Mandatory | Apply changes to files | 4.3BSD |
| pathchk | Filesystem | Mandatory | Check pathnames | |
| pax | Misc | Mandatory | Portable archive interchange | 4.4BSD[citation needed] |
| pr | Text processing | Mandatory | Print files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| printf | Shell programming | Mandatory | Write formatted output | 4.3BSD-Reno |
| prs | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Print an SCCS file | PWB UNIX |
| ps | Process management | Mandatory | Report process status | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| pwd | Filesystem | Mandatory | present working directory - Return working directory name | Version 5 AT&T UNIX |
| qalter | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Alter batch job | |
| qdel | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Delete batch jobs | |
| qhold | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Hold batch jobs | |
| qmove | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Move batch jobs | |
| qmsg | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Send message to batch jobs | |
| qrerun | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Rerun batch jobs | |
| qrls | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Release batch jobs | |
| qselect | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Select batch jobs | |
| qsig | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Signal batch jobs | |
| qstat | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Show status of batch jobs | |
| qsub | Batch utilities | Obsolescent (BE) | Submit a script | |
| read | Shell programming | Mandatory | Read a line from standard input | |
| renice | Process management | Mandatory | Set nice values of running processes | 4BSD |
| rm | Filesystem | Mandatory | Remove directory entries | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| rmdel | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Remove a delta from an SCCS file | PWB UNIX |
| rmdir | Filesystem | Mandatory | Remove directories, if they are empty. | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| sact | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Print current SCCS file-editing activity | System III |
| sccs | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Front end for the SCCS subsystem | 4.3BSD |
| sed | Text processing | Mandatory | Stream editor | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| sh | Shell programming | Mandatory | Shell, the standard command language interpreter | Version 7 AT&T UNIX (in earlier versions, sh was either the Thompson shell or the PWB shell) |
| sleep | Shell programming | Mandatory | Suspend execution for an interval | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| sort | Text processing | Mandatory | Sort, merge, or sequence check text files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| split | Misc | Mandatory | Split files into pieces | Version 3 AT&T UNIX |
| strings | C programming | Mandatory | Find printable strings in files | 2BSD |
| strip | C programming | Optional (SD) | Remove unnecessary information from executable files | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| stty | Misc | Mandatory | Set the options for a terminal | Version 2 AT&T UNIX |
| tabs | Misc | Mandatory | Set terminal tabs | PWB UNIX |
| tail | Text processing | Mandatory | Copy the last part of a file | PWB UNIX[citation needed] |
| talk | Misc | Optional (UP) | Talk to another user | 4.2BSD |
| tee | Shell programming | Mandatory | Duplicate the standard output | Version 5 AT&T UNIX |
| test | Shell programming | Mandatory | Evaluate expression | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| time | Process management | Mandatory | Time a simple command | Version 3 AT&T UNIX |
| touch | Filesystem | Mandatory | Change file access and modification times | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| tput | Misc | Mandatory | Change terminal characteristics | System V |
| tr | Text processing | Mandatory | Translate characters | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| true | Shell programming | Mandatory | Return true value | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| tsort | Text processing | Mandatory | Topological sort | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| tty | Misc | Mandatory | Return user's terminal name | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| type | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Displays how a name would be interpreted if used as a command | |
| ulimit | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Set or report file size limit | |
| umask | Misc | Mandatory | Get or set the file mode creation mask | System III |
| unalias | Misc | Mandatory | Remove alias definitions | |
| uname | Misc | Mandatory | Return system name | PWB UNIX |
| uncompress | Misc | Optional (XSI) | Expand compressed data | 4.3BSD |
| unexpand | Text processing | Mandatory | Convert spaces to tabs | 3BSD |
| unget | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Undo a previous get of an SCCS file | System III |
| uniq | Text processing | Mandatory | Report or filter out repeated lines in a file | Version 3 AT&T UNIX |
| unlink | Filesystem | Optional (XSI) | Call the unlink function | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| uucp | Network | Optional (UU) | System-to-system copy | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| uudecode | Network | Mandatory | Decode a binary file | 4BSD |
| uuencode | Network | Mandatory | Encode a binary file | 4BSD |
| uustat | Network | Optional (UU) | uucp status inquiry and job control | System III |
| uux | Process management | Optional (UU) | Remote command execution | Version 7 AT&T UNIX |
| val | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Validate SCCS files | System III |
| vi | Text processing | Optional (UP) | Screen-oriented (visual) display editor | 1BSD |
| wait | Process management | Mandatory | Await process completion | Version 4 AT&T UNIX |
| wc | Text processing | Mandatory | Line, word and byte or character count | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| what | SCCS | Optional (XSI) | Identify SCCS files | PWB UNIX |
| who | System administration | Mandatory | Display who is on the system | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| write | Misc | Mandatory | Write to another user's terminal | Version 1 AT&T UNIX |
| xargs | Shell programming | Mandatory | Construct argument lists and invoke utility | PWB UNIX |
| yacc | C programming | Optional (CD) | Yet another compiler compiler | PWB UNIX |
| zcat | Text processing | Optional (XSI) | Expand and concatenate data | 4.3BSD |
See also[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ^Stanfield, Vicki (2006). Linux System Administration. Craig Hunt Linux Library. Roderick W. Smith (2 ed.). John Wiley & Sons. p. 152. ISBN9780782152203. Retrieved 2012-11-27.
The command
sgis frequently a synonym fornewgrp.
External links[edit]
Basic Unix Commands Cheat Sheet.pdf
| The Wikibook Guide to UNIX has a page on the topic of: Commands |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Unix reference cards. |
- Rosetta Stone For *Nix – configurable list of equivalent programs for *nix systems.
- The Unix Acronym List – explains the names of many Unix commands.
The total number of Unix commands is immense. No normal user or system administrator would ever need to know them all.
The Unix commands available to you will vary based upon several factors:
- The version of Unix you are using (FreeBSD, Linux, Solaris, AIX, HP-UX, OpenBSD, etc…)
- The Unix shell you are using (sh, csh, tcsh, ksh, bash, etc…)
- The packages installed on the system and the way the system is configured
- Your access level on the system
This list of basic Unix commands will get you started using and learning Unix.
Chart of Basic Unix Commands
| Unix Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ls | List directory contents |
| cp | Copy files |
| rm | Remove directory entries |
| file | Determine file type |
| find | Walk a file hierarchy |
| which | Locate a program file in the user’s path |
| whereis | Locate programs |
| gcc, g++ | GNU project C and C++ Compiler |
| gdb | The GNU Debugger |
| less | View the contents of a text file |
| diff | Find differences between two files |
| cmp | Compare two files |
| vi | Text editor |
| chmod | Change file modes |
| man | Display the on-line manual pages |
| mv | Move and rename files |
| ispell | Interactive spelling checker |
| biff | Be notified if mail arrives and who it is from |
| lpr | Print a file |
| lpq | Show the print queue |
| ftp | Transfer a file to another Unix system |
| logout | Quit using the system |
| pwd | Print working directory name |
| cd | Change working directory |
| ln | Make a file link |
| mkdir | Make directories |
| rmdir | Remove directories |
| chmod | Change file modes |
| quota | Display disk usage and limits |
| history | Display a list of recent commands |
| ps | Show the status of processes |
| kill | Stop a running processes |
| passwd | Change your password |
| alias | Create a command alias |
| unalias | Delete a command alias |
| export | Set an environment variable |
| script | Record your terminal session to a file |
| bg | Send a job to the background |
| fg | Bring a job to the foreground |
| jobs | Print a list of current jobs |
The basic Unix commands are fairly standard across the various Unix platforms, although command arguments differ at times. In addition, the basic Unix commands vary between Unix shells.
Use the Unix `man` command to learn more about any of these commands.
Basic Unix Commands in Detail
mkdir
Create the DIRECTORY(ies), if they do not already exist.
Usage
mkdir [OPTION] DIRECTORY
Options
Note: Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-m, mode=MODE set permission mode (as in chmod), not rwxrwxrwx – umask
-p, parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed
-v, verbose print a message for each created directory
-help, display this help and exit
-version, output version information and exit
Examples
Create single directory
Create 3 directories
cd
Use cd to change directories. Type cd followed by the name of a directory to access that directory.Keep in mind that you are always in a directory and can navigate to directories hierarchically above or below.
Usage
cd DIRECTORYNAME
Example
mv
To change the name of a directory. Type mv followed by the current name of a directory and the new name of the directory.
Usage and Example
This renames the filejunkas the fileprecious.
pwd
print working directory; will show you the full path to the directory you are currently in. This is very handy to use, especially when you need to perform other directory related tasks.
Usage
pwd
Example:
rmdir
Remove an existing directory
Usage
rm DIRECTORYNAME
Options
rm -r
Removes directories and files within the directories recursively.
Example
To delete a directory named usersmith, type the following command ((from any directory except usersmith):
chown
change file owner and group; Change the owner and/or group of each FILE to OWNER and/or GROUP. With –reference, change the owner and group of each FILE to those of RFILE
Usage
chown [OPTION] OWNER[:[GROUP]] FILE
chown [OPTION] :GROUP FILE
chown [OPTION] –reference=RFILE FILE
Options
-c, changes like verbose but report only when a change is made
-dereference affect the referent of each symbolic link, rather than the symbolic link itself
-h, no-dereference affect each symbolic link instead of any referenced file (useful only on systems that can change the ownership of a symlink)
-from=CURRENT_OWNER:CURRENT_GROUP
change the owner and/or group of each file only if its current owner and/or group match those specified here. Either may be omitted, in which case a match is not required for the omitted attribute.
-no-preserve-root do not treat `/’ specially (the default)
-preserve-root fail to operate recursively on `/’
-f, -silent, -quiet suppress most error messages
Unix Basics Commands Pdf With Example
-reference=RFILE use RFILE’s owner and group rather than the specifying OWNER:GROUP values
-R, -recursive operate on files and directories recursively
-v, -verbose output a diagnostic for every file processed
The following options modify how a hierarchy is traversed when the -R option is also specified. If more than one is specified, only the final one takes effect.
-H if a command line argument is a symbolic link to a directory, traverse it
-L traverse every symbolic link to a directory encountered
-P do not traverse any symbolic links (default)
Examples
The owner of the ‘test.txt’ file is root, Change to new user hiox.
chmod
change file access permissions
Usage
chmod [-r] permissions filenames
r Change the permission on files that are in the subdirectories of the directory that you are currently in.
permission Specifies the rights that are being granted. Given below are the different rights that you can grant in an alphanumeric format.
u – User who owns the file.
g – Group that owns the file.
o – Other.
a – All.
r – Read the file.
w – Write or edit the file.
x – Execute or run the file as a program.
Numeric Permissions:
CHMOD can also to attributed by using Numeric Permissions:
400 read by owner
040 read by group
004 read by anybody (other)
200 write by owner
020 write by group
002 write by anybody
100 execute by owner
010 execute by group
001 execute by anybody
Examples
gives:
read, execute, and write access to the user (that’s you)
read and execute access to the group and
read and execute access to others
Basic Unix Linux Commands Pdf
The same can be achieved by using the command
ls
Short listing of directory contents
Usage
ls [OPTION]
Options
-a list hidden files
-d list the name of the current directory
-F show directories with a trailing ‘/’
executable files with a trailing ‘*’
-g show group ownership of file in long listing
-i print the inode number of each file
-l long listing giving details about files and directories
-R list all subdirectories encountered
-t sort by time modified instead of name
Example
To list the contents of the current directory:
cp
To copy files
Usage and Examples
Copy the files “myfile” to the file “yourfile” in the current working directory. This command will create the file “yourfile” if it doesn’t exist. It will normally overwrite it without warning if it exists.
With the “-i” option, if the file “yourfile” exists, you will be prompted before it is overwritten.
Copy the file “/data/myfile” to the current working directory and name it “myfile”. Prompt before overwriting the file.
Copy all files from the directory “srcdir” to the directory “destdir” preserving links (-doption), file attributes (-p option), and copy recursively (-r option). With these options, a directory and all it contents can be copied to another directory.
ln
Creates a symbolic link to a file.
Usage and Example
Creates a symbolic link named symlink that points to the file test.
Typing “ls -i test symlink” will show the two files are different with different inodes.
Basic Unix Commands For Beginners Pdf
Typing “ls -l test symlink” will show that symlink points to the file test.
locate
A fast database driven file locator.
<! >
<! >
Usage
locate [options] name(s)
Basic Unix Administration Commands Pdf
Options
-q – to suppress error messages
-n – followed by an integer, this option limits the results to a specific number
-i – performs a case-insensitive search
Examples
>locate '*.png'
Diplays all the files that have .png file extension.
>locate -n 15 '*.html'
Displays 15 results from a search for files with .html extension
>locate -i '*.HtmL'
Returns all files with extensions .html, .HTML or any such similar combination.